Algorithms and Data Structures
C Review 💻
Aryan Mediratta
Here's what we'll do.
Here's what we'll do.
A quick review of C fundamentals
Here's what we'll do.
A quick review of C fundamentals
Expressions, statements, lvalues, and rvalues
Here's what we'll do.
A quick review of C fundamentals
Expressions, statements, lvalues, and rvalues
Structs and Pointers
Here's what we'll do.
A quick review of C fundamentals
Expressions, statements, lvalues, and rvalues
Structs and Pointers
UNIX review and debugging
Here's what we'll do.
A quick review of C fundamentals
Expressions, statements, lvalues, and rvalues
Structs and Pointers
UNIX review and debugging
Good coding practices
The Build Process 🔧

Preprocessor Directive
Main Function
Function call to printf()
C Tokens 🎟️
Tokens are the smallest unit of a programming language.
C Tokens 🎟️
- Keywords 🔑
- Identifiers 🪪
- Constants 2️⃣
- Operators ➕
- Delimiters ✂️
C Keywords 🔑
- alignas (C23)
- alignof (C23)
- auto
- bool (C23)
- break
- case
- char
- const
- constexpr (C23)
- continue
- default
- do
- double
- else
- enum
- extern
- false (C23)
- float
- for
- goto
- if
- inline (C99)
- int
- long
- nullptr (C23)
- register
- restrict (C99)
- return
- short
- signed
- sizeof
- static
- static_assert (C23)
- struct
- switch
- thread_local (C23)
- true (C23)
- typedef
- typeof (C23)
- typeof_unqual (C23)
- union
- unsigned
- void
- volatile
- while
Primitive Types 🏷️
int - Integer [signed/unsigned, long/short]
char - Character (1 byte)
float - Single Precision Floating Point Number
double - Double Precision Floating Point Number
size_t - Return type of the sizeof() operator
void - No value
Variable Declaration
Variable Declaration with Initialization
Multiple Declarations of the same type
Control Statements 🎮
Conditionals
Control Statements 🎮
Conditionals
Switch Statements
YouTube: Why are Switch Statements So Fast? - Low Level Learning
Control Statements 🎮
Loops
While Loop
Control Statements 🎮
Loops
While Loop

Control Statements 🎮
Loops
Do-while Loop
Control Statements 🎮
Loops
Do-while Loop

Control Statements 🎮
Loops

Control Statements 🎮
Loops
Functions
Functions
Remember Recursion? 🤔
How did we recursively define the Fibonacci Sequence?
\( F_n = F_{n-1} + F_{n-2} \)
$F_0 = 0$
$F_1 = 1$
$0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, \cdots$
Let's turn it into code.
Implement a function int fibonacci(int n) that takes n as input and returns the nth Fibonacci number.
Expressions vs Statements
Expression
A piece of code that produces a value, or can be evaluated to get a value.
Can appear in any context where a value is allowed.
Statement
A complete instruction that can be executed.
Often separated by semicolon (;) unless they end with a code block.
Expressions vs Statements
Expressions can also be used as statements.
Assignments
Assignments are expressions!
They return a value.
Assignments are right-associative.
lvalues and rvalues
Assignments expressions are of the form lvalue = rvalue.
Expressions permitted on the left of = are lvalues.
They represent a place where a value can be stored.
Expressions permitted on the right of = are rvalues.
Just a value.
All lvalues are rvalues but not all rvalues are lvalues.

Source: XKCD, Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 2.5 License
Pointers and Indirection 👉
Pointers store the location of variables in memory.
Every data type has a corresponding pointer type, which can be invoked using the * operator.
A variable directly refers to its value (as an lvalue).
A pointer does so indirectly.
Pointers and Indirection 👉
We can have pointers to pointers, and pointers to pointers to pointers.
Did we just start counting? 😕
Pointers and Indirection 👉
The value at the location stored in a pointer can be accessed (as an lvalue) by dereferencing it.
Dereference Operator: *
NULL (or in C23, nullptr) is a special value for a pointer that points to nothing.
Dereferencing a null pointer is a guaranteed way to get a segfault.
Arrays 🎞️
Arrays are contiguously stored ordered collections of a type.
They can be stack-allocated or heap-allocated.
Stack Allocated Arrays 📦
In order for anything to be allocated on the stack, its size must be known at compile-time (well, kind of).
Some C versions support Variable Length Arrays (VLAs), but they're not portable and should be avoided for robust code.
Structures 🏢
Structures help define our own compound datatypes as combinations of primitive types.
They are like classes but can only contain member variables and not functions/methods.
Structures 🏢
Structures 🏢
Dynamic Memory Allocation
Memory on the heap can be allocated using malloc().
If you also want it initialized to 0, you can use calloc().
To resize heap-allocated memory, use realloc().
All memory allocated using these functions must be freed using free(). Failing to do so produces a memory leak.
Dereferencing with Arrays
The name of an array resolves to its address.
Or more precisely, the address of its first element.
array[i] is just syntactical sugar for *(array + i).
Dynamically Allocating 2D Arrays
Freeing Dynamically Allocated 2D Arrays
Strings
C does not (really) have a built-in string data type.
Instead, we have arrays of characters.
Strings in C are just character arrays that end with the null terminator.
printf with %s and other string functions stop when they see '\0'.
What data type is this? 🤔
char *var[6];
It's an array of pointers!
Passing Pointer Arrays
Command-Line Arguments
Command-Line Arguments are passed to the main function as a pointer array.
To use command-line arguments, use this signature for the main function
Command-Line Arguments

UNIX Review and Debugging
Shell Commands
Redirection
command > output_file.txt
command < input_file.txt
command < input_file.txt > output_file.txt
Redirection: Output Demo
Redirection: Input Demo
Matching Expected Outputs and Diff
- Sometimes, you need your program’s behavior to exactly match a given format.
- Often, your programs will be run by other programs, rather than humans.
- Humans can easily process slight differences in output. Computers? Not so much.
Matching Expected Outputs and Diff
Say we want to print a 2D array.
------------------------- | 2| 4| 5| 6| 7| 9| | 10|-23| 4| 5| 2| 7| | 0| 3| 10| 33|234| 40| -------------------------
Implement void print_array(int* arr[], int rows, int cols) using this output format.
Matching Expected Outputs and Diff
Checking that we did it right!
The diff command takes two files and tells if they are identical, and optionally tells where they differ, if they do.
$ diff file1 file2
$ diff your_output.txt expected_output.txt
GDB Commands
| break | Set a breakpoint |
Print the value of a variable/expression | |
| next | Execute next line (step over if function) |
| step | Execute next line (step into if function) |
| run | Start execution of the program |
| continue | Continue execution until next breakpoint/end of program |
| watch | Break when a variable/expression changes value |
| list | Display source code |
| quit | Exit out of GDB |
Reverse Debugging
Common Errors
Common Errors
Common Errors
Good Coding Practices
Indent your code properly.
Use meaningful variable names.
Avoid using magic numbers.
Initialize your variables to avoid undefined behavior.
Try to make your code self-documenting, but comment when appropriate.
Try to limit functions to small tasks.
Good Coding Practices
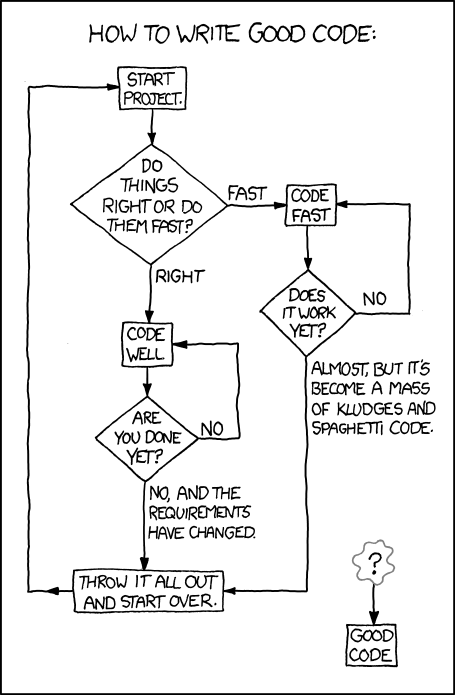
Source: XKCD, Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 2.5 License
Topics Not Covered Here
- Strings and the string.h library
- File Handling
- Bit Manipulation and Bitmasking
- const